Tomado de: https://rlaput.github.io/Azure-GitLab-Autodeploy/
Deploying an application from GitLab to Azure App Service
This post is about deploying an application from GitLab source control to Azure App Service. Since this post is just to show you how to do it, you should already have intermediate knowledge on the following:
Azure App Service Deployment Source Control Options
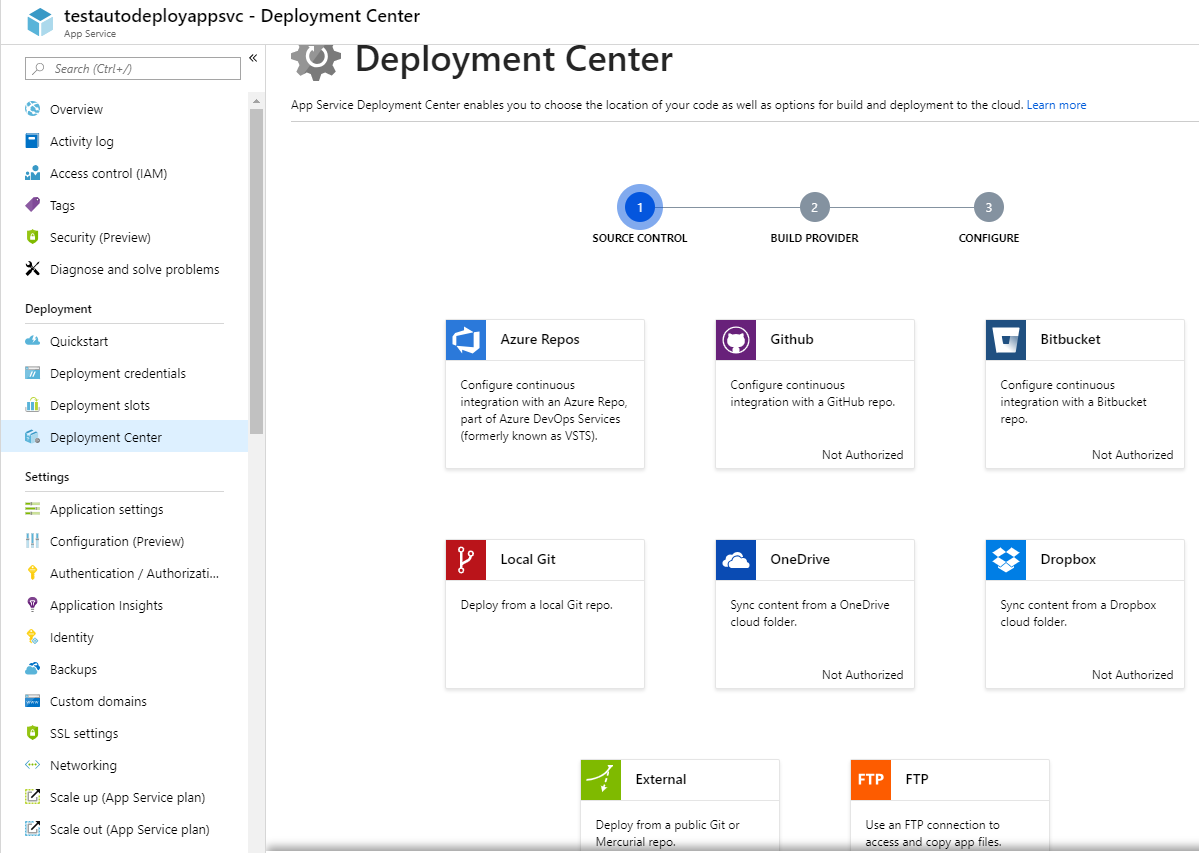
As you can see in the image above, GitLab is not in the choices. We will be using the External option in this post.
Generating SSH Key From Kudu
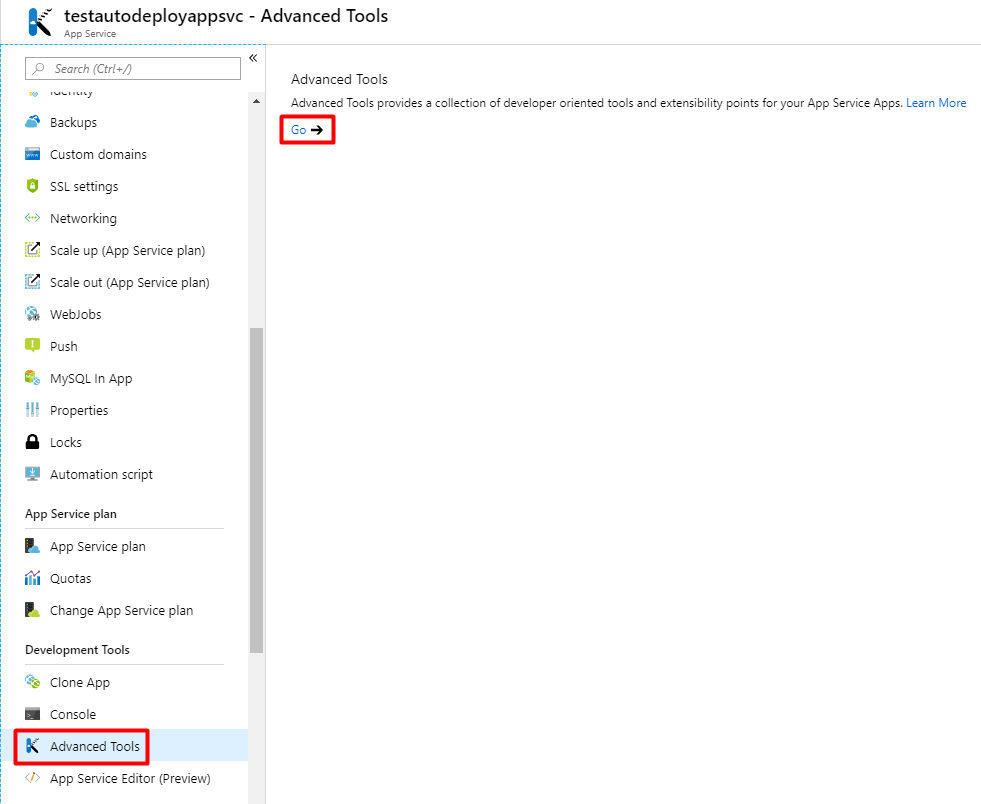
In your Azure portal, click on your App Service and scroll down to Development Tools option group. Choose Advanced Tools and click Go.
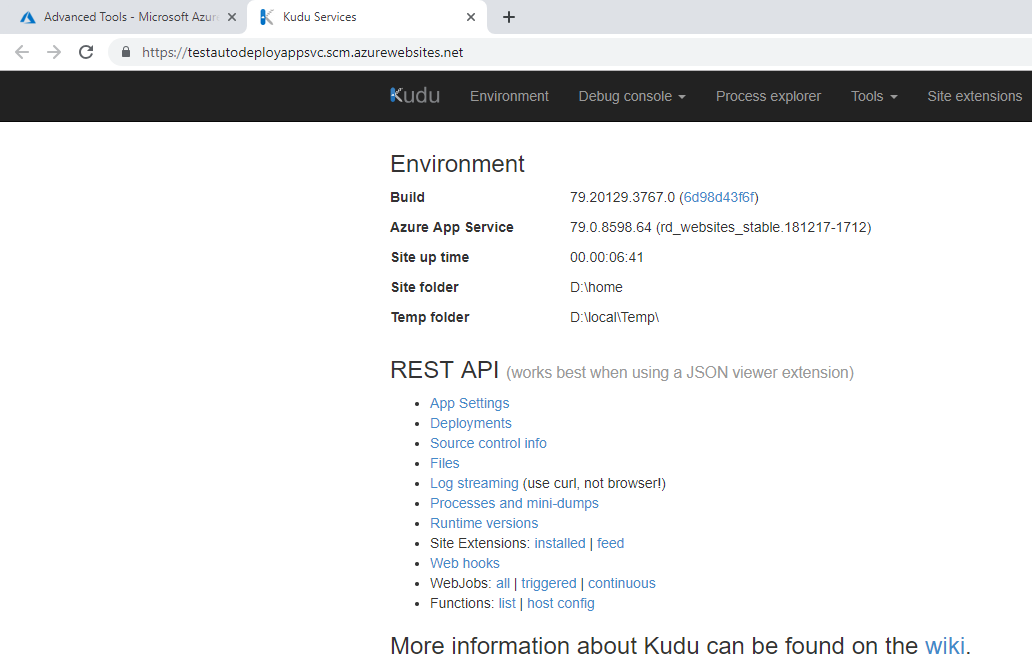
You will be redirected to Kudu Services for your App Service:
Add /api/sshkey?ensurePublicKey=1 to the url above to generate a public SSH key for the app service. Press enter.
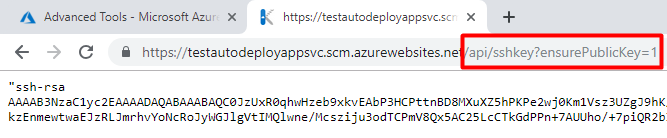
You will be navigated to a very simple page with the text "ssh-rsa <hashed string here>". Copy the text without the beginning and trailing quotation marks to a text editor. We will use this later on.
Setting Up Deploy Keys in GitLab
Navigate to your project in GitLab. Go to Settings->Repository.
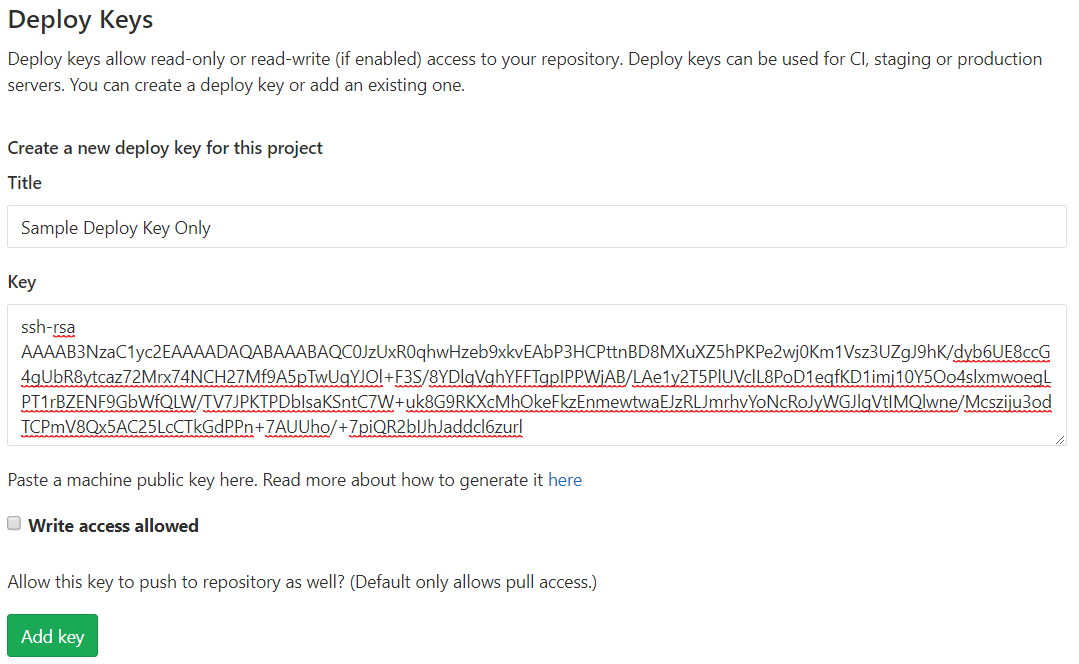
Expand Deploy Keys. Input your desired deploy key name in the Title field. Paste the generated public SSH key from Kudu into the Key field. Leave the Write access allowed checkbox unchecked (since we only need to give read access to Kudu for deployment) and click Add key.
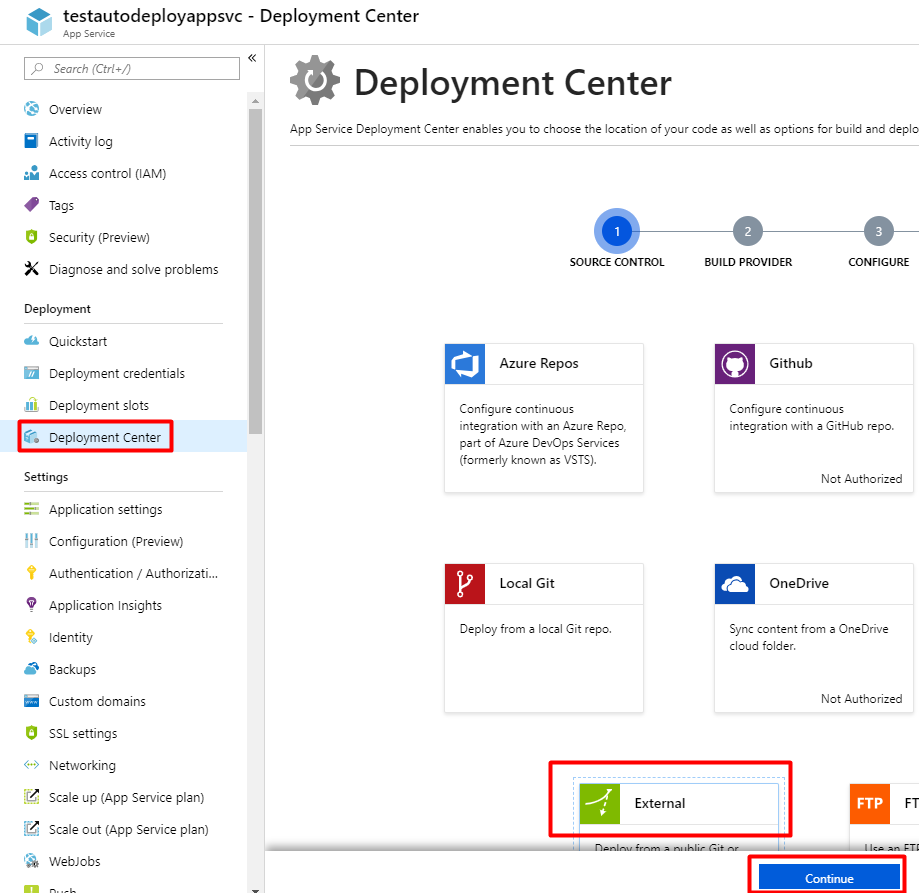
Adding GitLab Project as Deployment Source In Azure Portal
Navigate to you App Service in Azure Portal. Open Deployment Center, choose External, then click Continue.
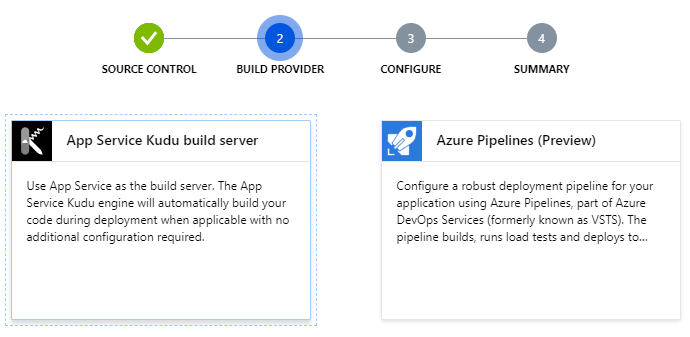
Choose App Service Kudu build server as build provider then continue.
Copy your GitLab project SSH Url.
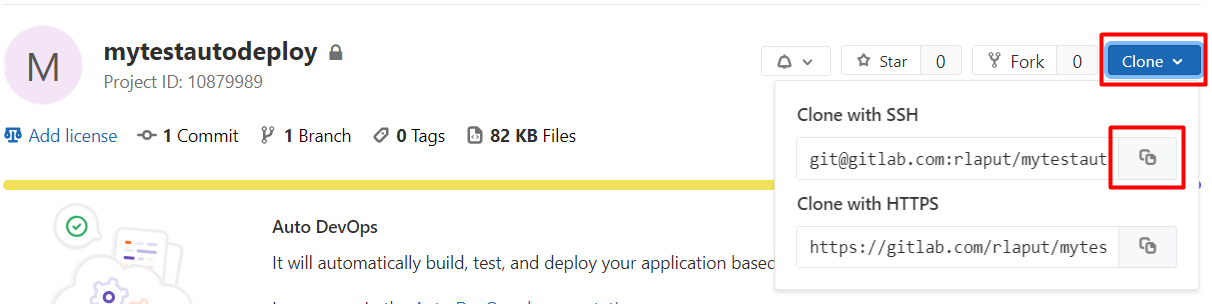
Paste it into the Repository field. Enter branch name to be deployed. Choose Git for repository type. Continue and Finish.
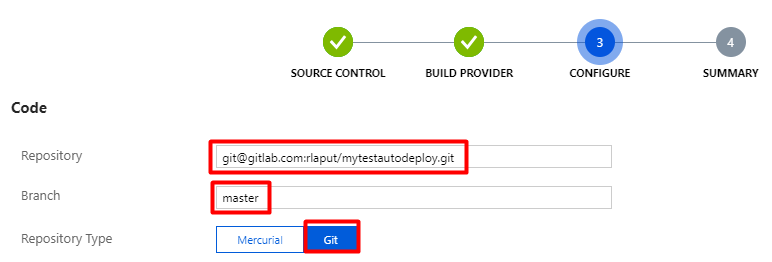
Wait for a few seconds and let Azure deploy your app. Status will change to Success when the deployment succeeds. If there are new changes to master branch, click on Sync so that Azure will pull and deploy the latest changes.
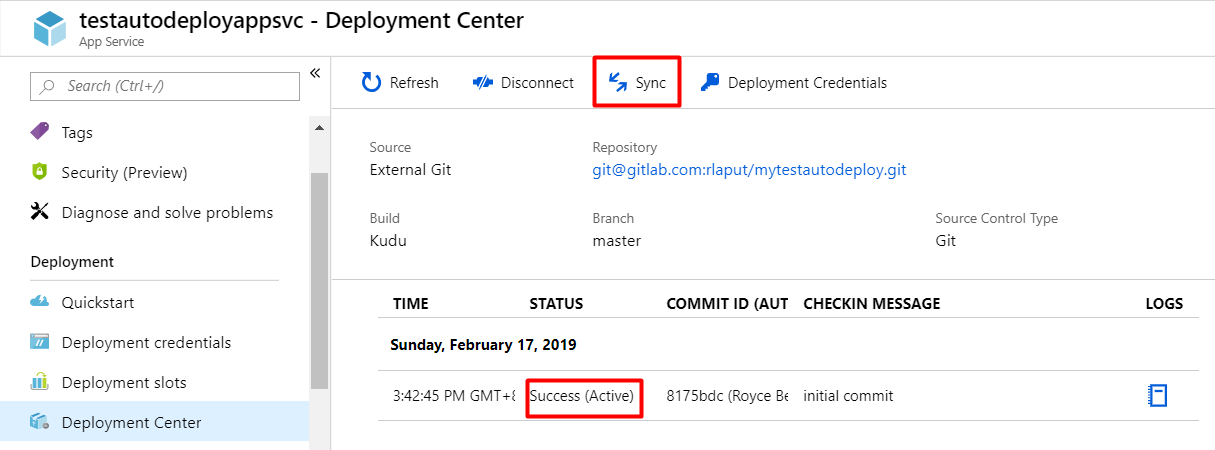
Auto-Deployment using Webhook
The steps above allow us to deploy an application from source control manually using Azure portal. The next procedures will allow us to automate the deployment to Azure everytime there are new changes in that branch using webhooks.
First, we need our app credentials so that our webhook can authenticate to Kudu and let it deploy our application using its deploy endpoint. Go to Deployment Center, click on Deployment Credentials beside Sync, then copy the password.
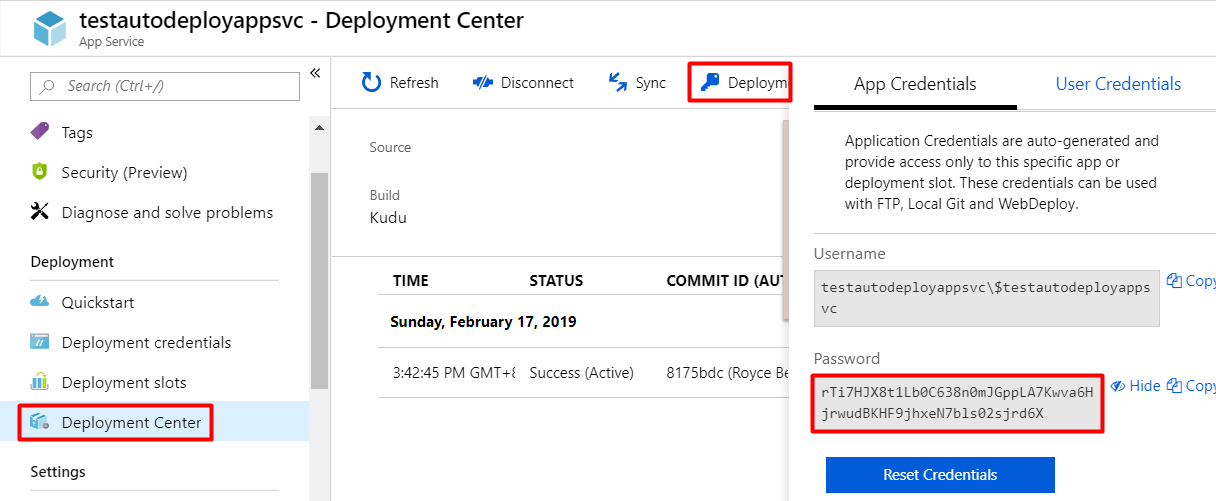
The deploy endpoint format:
https://$<sitename>:<password>@<sitename>.scm.azurewebsites.net/deploy
Replace <sitename> with your App Service name and <password> with the password you copied from deployment credentials. Example: https://$testautodeployappsvc:rTi7HJX8t1Lb0C638n0mJGppLA7Kwva6HjrwudBKHF9jhxeN7bls02sjrd6X@testautodeployappsvc.scm.azurewebsites.net/deploy
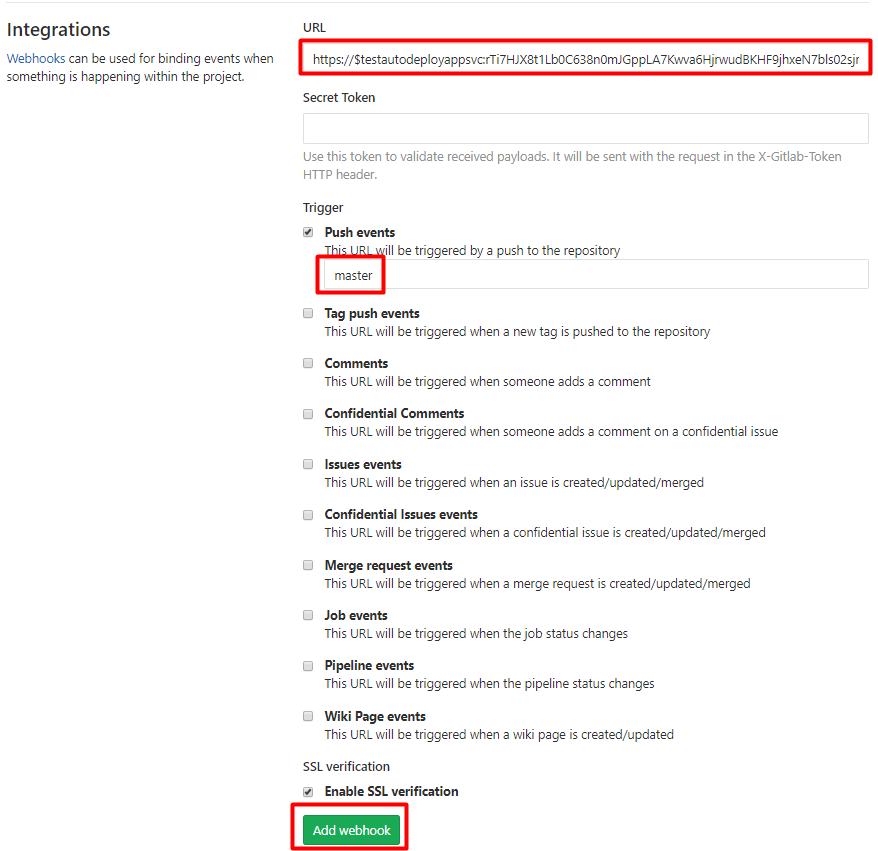
Navigate to your project in GitLab, go to Settings->Integrations. Input the constructed url above based on your site name and password. Check Push events and input master in the field. This means that deployment webhook will be triggered when there is a push event in master branch. Finally, click Add webhook button.
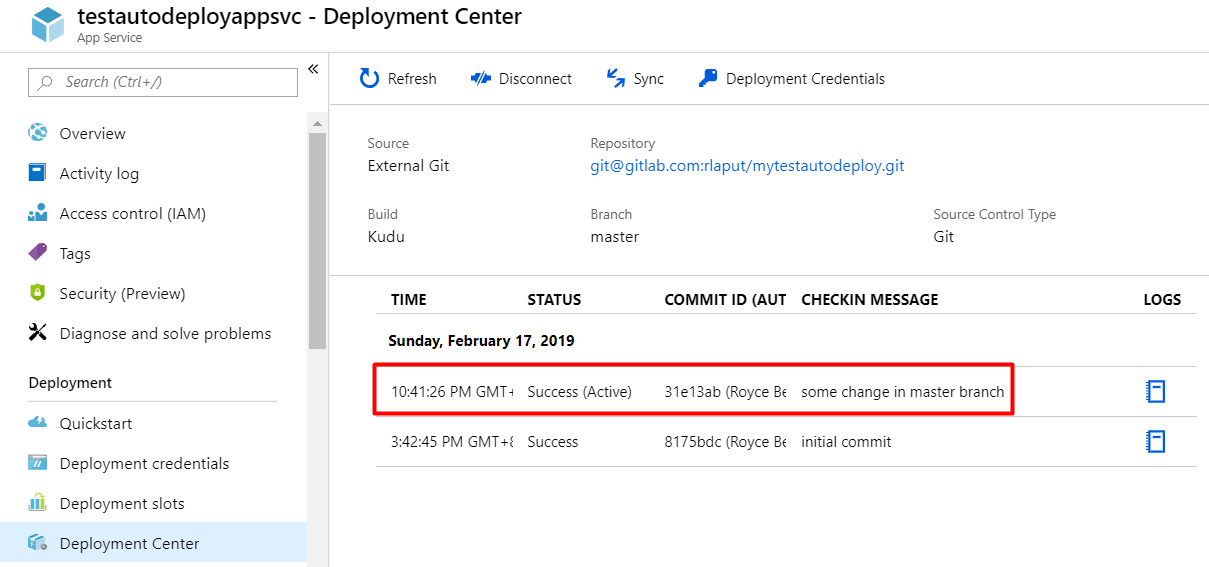
Now, I tried pushing a commit in master branch with comment message some change in master branch. Upon checking Deployment Center, the latest change has been deployed automatically without clicking Sync button.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario